Basic E-Bike Classifications
- E-Bike - A bicycle equipped with an electric motor that provides assistance when pedaling or through a throttle, depending on the class.
- Pedelec - Short for "pedal electric cycle," a type of e-bike that only provides assistance when the rider is pedaling (synonymous with Class 1 e-bikes in North America).
- Class 1 E-Bike - Provides pedal assistance only (no throttle) up to 20 mph. These e-bikes typically have access to most bike paths and trails.
- Class 2 E-Bike - Features both pedal assistance and throttle operation, with a maximum assisted speed of 20 mph.
- Class 3 E-Bike - Provides pedal assistance (usually no throttle) up to 28 mph. May have restricted access to certain bike paths and trails.
- S-Pedelec - A speed pedelec that can assist up to 28 mph (similar to Class 3, but common terminology in Europe).
- Speed Pedelec - An e-bike designed to assist at higher speeds, usually up to 28 mph or more in some regions.
- E-MTB - Electric mountain bike designed for off-road trails with features like suspension and wider tires.
- E-Road Bike - An electric road bike designed for paved surfaces with drop handlebars and narrower tires.
- E-Cargo Bike - An electric bicycle designed to carry heavy loads or passengers, featuring reinforced frames and extended wheelbases.
Motor System Components
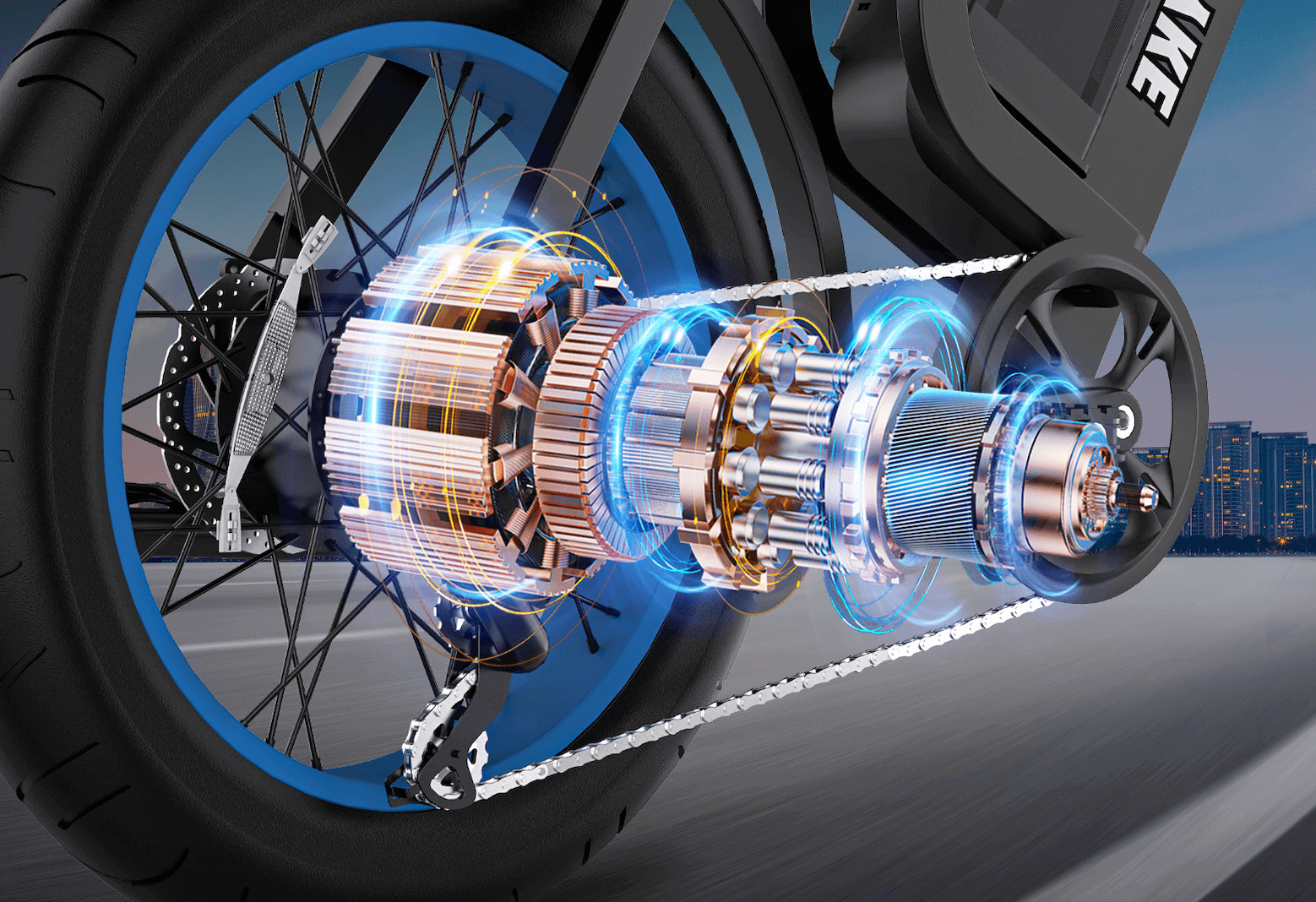
- Motor - The electric engine that provides power assistance to the e-bike, typically rated in watts.
- Motor Controller - The "brain" of the e-bike that regulates power flow from the battery to the motor based on rider input and sensor readings.
- Mid-Drive Motor - A motor positioned at the bike's bottom bracket, providing power directly to the drivetrain for efficient operation, especially on hills.
- Hub Motor - A motor built into either the front or rear wheel hub, providing direct power to that wheel.
- Rear Hub Motor - A motor integrated into the rear wheel, providing direct drive without using the bike's gears.
- Front Hub Motor - A motor built into the front wheel, creating an all-wheel-drive effect when combined with rear-wheel pedaling.
- Geared Hub Motor - A hub motor that uses internal gearing to provide more torque while maintaining efficiency and a smaller size.
- Direct Drive Hub Motor - A hubless motor where the axle itself is the motor's stator, offering smooth operation and potential regenerative braking.
- Motor Wattage - The power rating of an e-bike motor, typically ranging from 250W to 1000W depending on local regulations and intended use.
- Nominal Power - The continuous power output that a motor can sustain without overheating, as opposed to peak power.
- Peak Power - The maximum power output a motor can produce for short bursts, often 2-3 times higher than nominal power.
- Torque - The rotational force produced by the motor, measured in Newton meters (Nm), determining the bike's ability to climb hills and accelerate.
- Cadence Sensor - A device that detects pedaling motion to activate motor assistance, without measuring how hard you're pedaling.
- Torque Sensor - A sophisticated sensor that measures how much force is applied to the pedals, providing proportional motor assistance.
- Integrated Motor System - A proprietary motor design built specifically for a particular e-bike frame, often with matching battery and controller.
Battery and Power Management
- Battery - The rechargeable power source for the e-bike's motor, typically lithium-ion in modern e-bikes.
- Battery Capacity - The amount of energy a battery can store, measured in watt-hours (Wh), determining potential range.
- Watt-Hour (Wh) - Unit of energy equal to one watt of power sustained for one hour, calculated by multiplying voltage by amp-hours.
- Voltage (V) - The electrical potential of the battery, commonly 36V, 48V, or 52V in e-bikes, with higher voltage typically providing more power.
- Amp-Hour (Ah) - A measure of battery capacity indicating how many hours a battery can sustain a one-amp current.
- Battery Management System (BMS) - Electronic system that monitors and protects the battery from damage due to overcharging, over-discharging, or temperature extremes.
- Lithium-Ion Battery - The most common type of e-bike battery, offering high energy density and relatively low weight.
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) - A type of lithium battery known for longer lifespan and better safety, though typically heavier than standard lithium-ion.
- Battery Range - The distance an e-bike can travel on a single charge, affected by factors like terrain, rider weight, assistance level, and weather.
- Range Anxiety - The fear of running out of battery power before reaching your destination.
- Range Extender - An auxiliary battery that can be added to increase the distance an e-bike can travel on a single charge.
- Integrated Battery - A battery built into the frame of the e-bike for improved aesthetics and weight distribution.
- Removable Battery - A battery that can be detached from the e-bike for charging or security purposes.
- Battery Cycle - One complete discharge and recharge of a battery; lithium-ion batteries typically last 500-1000 cycles before significant capacity loss.
- Fast Charging - Technology that allows batteries to charge more quickly, often reaching 80% capacity in under an hour with compatible equipment.
- Charge Time - The duration required to fully charge a depleted battery, typically 3-6 hours for standard chargers.
- Battery Indicator - A display showing the remaining battery capacity, often as a percentage or battery symbol.
- Battery Discharge Rate - The speed at which a battery delivers power, affecting performance particularly during high-demand situations.
- Smart Battery - A battery with integrated electronics for monitoring health, usage patterns, and communication with the e-bike system.
- Power Management - Software systems that optimize battery usage based on riding conditions and user preferences.
Rider Interface and Controls
- Display - The screen on an e-bike that shows information such as speed, battery level, distance, and assistance level.
- LCD Display - A liquid crystal display screen showing ride data, often with backlight for visibility in various light conditions.
- Control Unit - The combination of buttons, switches, and display used to operate the e-bike's electronic systems.
- Assist Level - The degree of motor power provided relative to pedaling input, typically adjustable through multiple settings.
- Eco Mode - The lowest assistance level, providing minimal motor support to maximize battery range.
- Boost/Turbo Mode - The highest assistance level, providing maximum motor support at the expense of battery life.
- Throttle - A control (twist grip or thumb paddle) that activates the motor without pedaling, common on Class 2 e-bikes.
- Remote Control - A handlebar-mounted device for changing settings without removing hands from the grip.
- Pedal Assist System (PAS) - The system that automatically provides motor power when pedaling is detected.
- Bluetooth Connectivity - Wireless technology allowing e-bikes to connect with smartphones for additional features and customization.
- E-Bike App - A smartphone application that interfaces with the e-bike for customization, diagnostics, or navigation features.
- User Profile - Saved rider preferences for motor assistance, display settings, and other customizable features.
- Walk Mode - A feature that provides low-power motor assistance (usually up to 3.7 mph/6 kph) to help push the bike when walking alongside it.
- Power Switch - The main on/off button for the e-bike's electrical system.
- Motor Cut-Off - Safety feature that stops motor assistance when brakes are applied or in emergency situations.
Performance and Riding Mechanics
- Assisted Range - The distance an e-bike can travel with motor assistance on a single battery charge.
- Efficiency - How effectively an e-bike converts battery energy into forward motion, typically measured in watt-hours per mile (Wh/mi).
- Cadence - The rate at which a cyclist pedals, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
- Optimal Cadence - The pedaling rate (typically 60-90 RPM) that provides the most efficient power output and motor assistance.
- Regenerative Braking - A system that recaptures energy during braking to recharge the battery, available on some direct drive motor systems.
- Motor Inhibitor - A safety feature that cuts motor power when the brakes are applied.
- Mechanical Advantage - The benefit gained from using the bike's gears in combination with motor assistance for optimal efficiency.
- Range Estimate - The projected distance an e-bike can travel based on current battery level, assist mode, and riding conditions.
- Eco-Riding - Techniques for maximizing battery range, such as maintaining steady speeds and using lower assistance levels.
- Smart Range Management - Automated systems that adjust motor output to ensure you reach a specified destination without depleting the battery.
- Pedal-Feel - The sensation experienced when pedaling an e-bike, which varies between models from natural to mechanically assisted.
- Power-to-Weight Ratio - The relation between an e-bike's motor power and total weight, affecting performance particularly on hills.
- Dynamic Power Distribution - Advanced systems that adjust motor output based on riding conditions like incline, wind, and rider input.
- Speed Limit - The maximum velocity at which the motor provides assistance, determined by e-bike class and local regulations.
- Speed Sensor - A device that measures the rotation of the wheels to determine the bike's speed.
Technical and Maintenance Terms
- Firmware - The software embedded in the e-bike's controller that governs its operation and features.
- Firmware Update - Software improvements provided by manufacturers to enhance performance, fix issues, or add features.
- Diagnostic Tool - Software or hardware used to identify and troubleshoot e-bike system problems.
- Error Code - Numeric or symbolic representation of a specific system fault, displayed to help diagnose issues.
- Waterproof Rating (IP Code) - A two-digit number indicating how resistant electronic components are to water and dust ingress.
- Motor Declination - The reduction in motor performance as the battery level decreases.
- Thermal Management - Systems designed to prevent overheating of the motor, battery, or controller during intensive use.
- Battery Balancing - The process of equalizing charge across all cells in a battery pack to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Preventative Maintenance - Regular check-ups and maintenance procedures to prevent system failures and extend e-bike lifespan.
- System Integration - How well the motor, battery, and other electronic components work together for optimal performance.
- Proprietary System - E-bike components designed to work exclusively with specific brands or models, often requiring brand-specific parts for replacement.
- Open System - E-bike designs that use standardized components compatible across multiple brands for easier customization and repair.
- Motor Bearing - A crucial component that allows the motor shaft to rotate smoothly, requiring occasional maintenance.
- Warranty Period - The time during which the manufacturer will repair or replace defective components at no cost.
- Deep Discharge - Draining a battery below recommended levels, which can permanently damage lithium-ion batteries.
Legal and Safety Terms
- Street Legal - An e-bike that meets local regulations for legal road use, including power limitations and equipment requirements.
- Throttle Restriction - Limitations on throttle functionality to comply with local regulations, often implemented via firmware.
- Speed Governor - A device or software that prevents an e-bike from exceeding legally defined speed limits.
- Anti-Tampering Measures - Design features that prevent unauthorized modification of e-bike power or speed limitations.
- UL Certification - Safety certification from Underwriters Laboratories, indicating compliance with specific safety standards.
- CE Marking - European certification indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- Type Approval - A regulatory process in some regions requiring pre-approval of e-bike designs before they can be sold.
- Off-Road Designation - Classification indicating an e-bike is designed for trail use rather than public roads, sometimes with different regulatory requirements.
- Insurance Requirement - Legal obligation in some regions to have liability insurance when operating certain classes of e-bikes.
- Homologation - The approval process that certifies a vehicle meets regulatory standards for a specific market or region.
Conclusion
Mastering these 100 terms will give you a solid foundation for understanding e-bike technology, making informed purchasing decisions, and troubleshooting common issues. As e-bike technology continues to evolve rapidly, staying informed about the latest developments will enhance your riding experience and help you get the most from your electric bicycle.
Remember that e-bike terminology can vary slightly between regions and manufacturers, so always refer to your user manual for specific definitions pertaining to your model. Happy riding!
For more in-depth information on e-bike technology and maintenance, check out these additional resources:

Share:
Electric Bicycle Emergency Handling: Preventing and Responding to Common Dangers
DIY E-Bike Repair: 10 Common Problems Beginners Can Fix Themselves